Fractured Teeth

Fractured Teeth
Fractured Deciduous Teeth
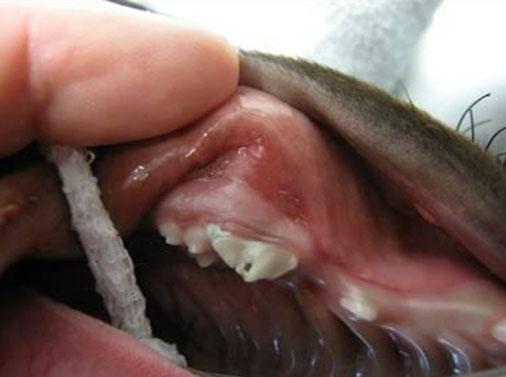
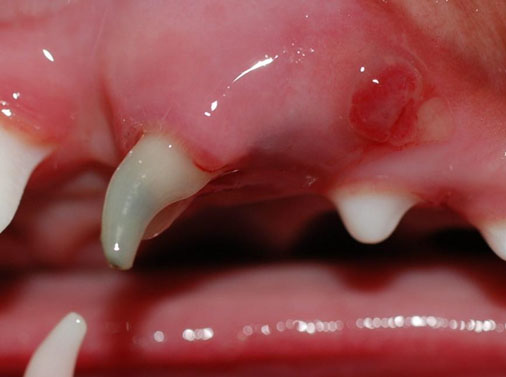
- Since deciduous teeth are more delicate compared to adult teeth and most of these deciduous or “baby” teeth are mostly made up of pulp tissue, if these teeth are fractured, there is a significant possibility that there will be pulp exposure and thus these teeth are dead and infected.
- Since these deciduous teeth are so closely associated with their developing adult tooth (the adult tooth bud), this could cause infection and thus malformation of the adult tooth in this area.
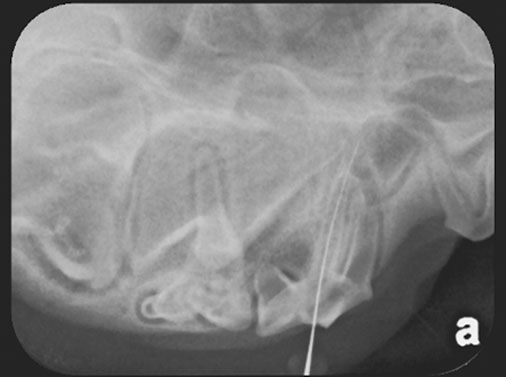
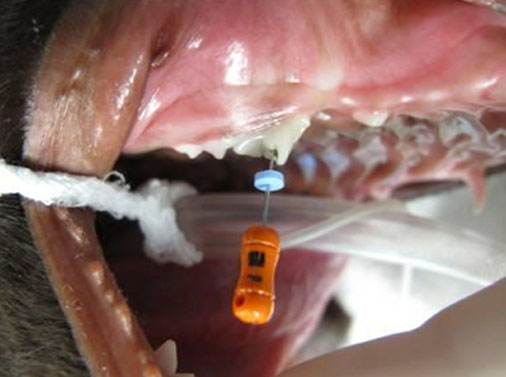
- In these pictures, a Pathfinder endodontic file shows communication with a developing adult tooth bud through its fracture site of the crown of the deciduous tooth.